
Articles
Tenses

What is a Tense?
 Tense is used to show the relation between the action or the state described by the verb and the time which is reflected in the form of the verb. There are three basic tenses in the English language. These are Present, Past and Future
Tense is used to show the relation between the action or the state described by the verb and the time which is reflected in the form of the verb. There are three basic tenses in the English language. These are Present, Past and Future
This is a verb form that indicates or can indicate a relation between the time the action in the verb occurs and the time the verb is uttered. A verb tense can also give an indication of the duration of the verb’s action and when or if it is completed.
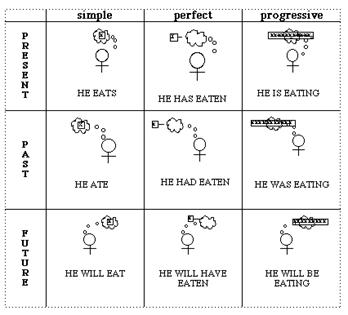
Simple Present Tense
We use simple present tense when the action is general and the action happens all the time in the past, present and future. Action is not always happening now and the statement is always true.
Example:
• Rohan drives a Maruti
• We read everyday.
• She meets her friends in the park.
Present Perfect Tense
This is a grammatical combination of present tense and the perfect aspect, used to express a past event that has present consequences. It is a compound tense in English. The events described by present perfects are not necessarily completed.
Present perfect is used to describe an experience. It is also used to talk about change that has happened over a period of time. Often present perfect is used to list the accomplishments of individuals and humanity. Here specific time is not mentioned. When we are still waiting for the action to happen we can use present perfect. It can also be used to talk about different actions that happened at different times in the past.
Example:
• Ria has never been here.
Example:
• He has improved in Math since last year.
• Lata hasn’t finished reading the book as yet.
Present Progressive Tense
This indicates continuing action, something that is going on now. It indicates actions happening at the time of speaking or right now. It can be used to talk about actions occurring over a period of time which includes the present. However it may not necessarily be this very moment. It is sometimes used to indicate ongoing, developing, imminent or future actions. Present progressive tense may be used to talk about actions happening in the near future especially for planned future events.
Example:
• I am growing to like this place
• John is playing piano.
• She is seeing her doctor tomorrow.
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
This is similar to the present perfect tense except that the action is continuous. It describes something that starts in the past and continues into the present.
Example:
- He has been practicing violin all day.
- She has been teaching French for the last ten years.
- I have been exercising from the morning.
Simple Past Tense
This is used to talk about events that happened at a specific time in the past. A time adverb is used in order to indicate when it happened. It can also be used to describe events that happened over a period of time in the past but not now. It may be used to talk about repeated actions that took place in the past. Simple past talks about a completed action in a time before now. Duration is not important. It can be the distant or the recent past
Example:
• I left school in 1996.
• They lived in North Carolina for seven years.
• We always went boating during vacations.
Past Perfect Tense
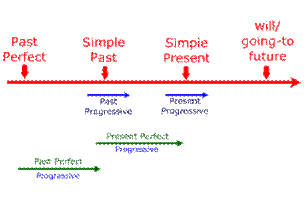 This is used in English when we are relating two events which happened in the past. It helps to show which event happened first. This tense is formed using two components, the verb has (in the past tense) and the past participle form of a verb. With a regular verb the past participle ends with a “ed.” This is formed with the helping verb had. This shows an action that came before another action in the past.
This is used in English when we are relating two events which happened in the past. It helps to show which event happened first. This tense is formed using two components, the verb has (in the past tense) and the past participle form of a verb. With a regular verb the past participle ends with a “ed.” This is formed with the helping verb had. This shows an action that came before another action in the past.
Example:
- The postman had brought a parcel before we arrived.
- He had to appear for many interviews before he got a job.
- I had left when she walked into the house.
Past Progressive Tense
This indicates continuing action, something that was happening or going on in the past. This tense is formed with the helping ‘to be’ verb in the past tense plus the past participle of the verb with an –ing ending. This puts emphasis on the course of action in the past, two actions happening at the same time in the past and action going on at a certain time in the past.
Example:
• He was working hard in the garage all day.
• When he was having his lunch, the postman knocked at the door.
• We were walking through the woods this afternoon.
Past Perfect Progressive Tense
This indicates a continuous action which was completed at some point of time in the past. It is formed with the modal had and been plus the present participle of the verb with an-ing ending.
Example:
- She was pottering around in the kitchen all morning before …………………..the guests arrived.
- He has been stealing all these years before the police caught him.
- They had been campaigning all these months but they lost the elections.
Simple Future Tense
This is used to talk about things that will happen at a later time than now.
Using ‘be going’ is one way to form the future simple tense. Another way is to use will. When we use will/shall for prediction they combine with verbs to form tenses in the ordinary way.
Example:
• I am going to the theatre tomorrow.
• The students will stage a show next week.
• I shall see her on Monday.
Future Perfect Tense
This is used to describe an event that is expected or planned to happen before another event in the future. We use future perfect tense when we want to emphasize ‘no later than’. It puts a ‘no later than’ limit on when the action will be completed. It is a verb form which expresses action completed by a specified time in the future.
Example:
- By 7pm this evening they will have left for Paris.
- He will have cooked dinner by 6pm tomorrow.
- They will have spent a week in Chennai by then.
Future Continuous Tense
This expresses action at a particular moment in the future. The action will start before that moment but will not have finished at that moment. It emphasizes an action or event that will be in progress at some time in the future. Here present continuous tense is recycled.
Example:
• I will be practising guitar at 5pm tomorrow.
Example:
• The baby will be sleeping when they come.
• They will not be walking by the river this evening.
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
This indicates a continuous action that will be completed at some point in future. This is formed by the modal “will” plus “have” plus “been” plus the present participle of the verb(with an –ing ending)
Example:
- They will have been playing cricket for two hours by …………………..evening.
- He will have been studying law for a few months by June.
- By December he will have been working in the company for 10years.
Want to know more about Tenses? Click here to schedule a live help with an eTutor!
****
About eAge Tutoring:
eAgeTutor.com is the premium online tutoring provider. Using materials developed by highly qualified educators and leading content developers, a team of top-notch software experts, and a group of passionate educators, eAgeTutor works to ensure the success and satisfaction of all of its students.
Contact us today to learn more about our guaranteed results and discuss how we can help make the dreams of the student in your life come true!
Reference Links:
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Determiner_%28linguistics%29
- http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-T4xw5C74Ps
- http://www.englishclub.com/grammar/verb-tenses.htm
- http://www.learnenglish.de/grammar/tensetext.htm
- http://leo.stcloudstate.edu/grammar/tenses.html
